Understanding Prosthetic Abandonment
Share
By Monica Espinosa and Dan Nathan-Roberts, Ph.D.
Industrial and Systems Engineering, San José State University
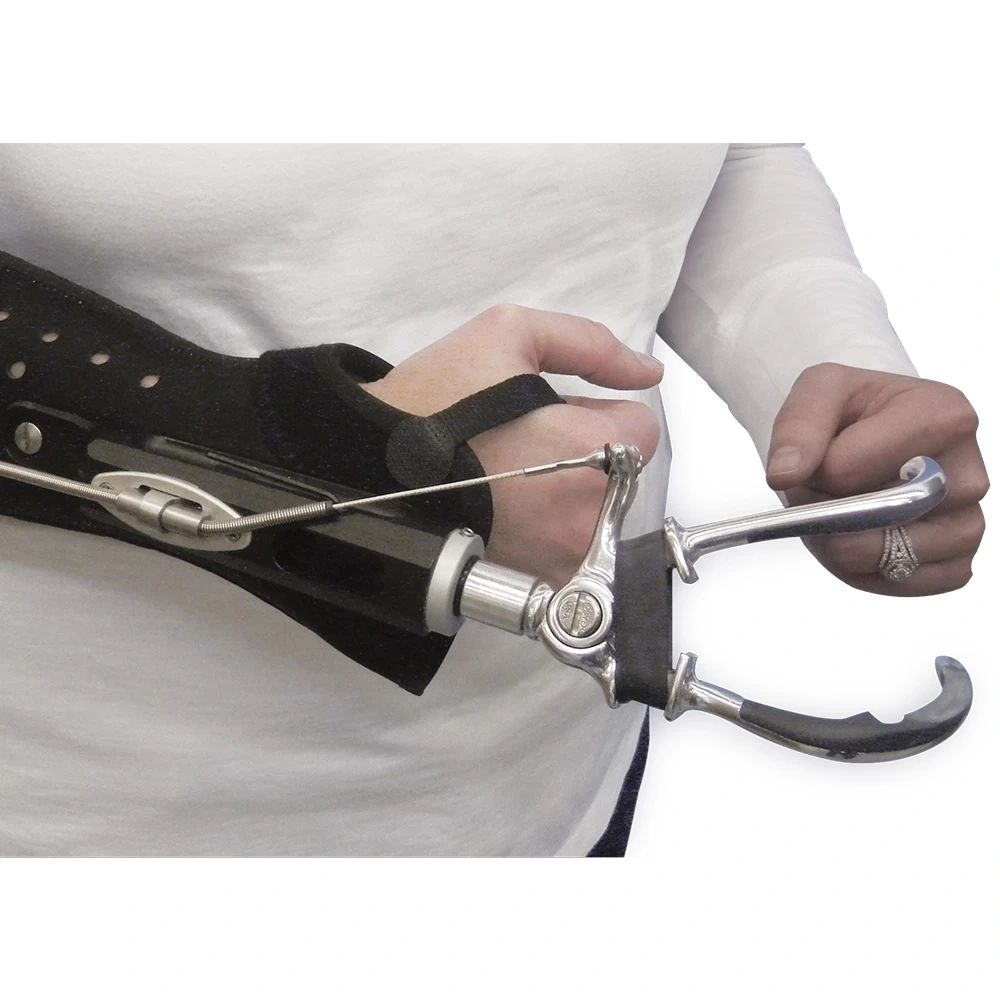
Prosthetics have come a long way in offering enhanced functionality and independence to individuals with limb amputations. Despite these advancements, a significant number of users still abandon their prosthetic devices. This phenomenon highlights the need to delve deeper into the reasons behind this trend and find ways to improve the user experience.
The Current Landscape of Prosthetic Use
In 2007, the National Limb Loss Information Center estimated that 1.7 million people in the United States had experienced limb loss, with projections indicating a 131% increase by 2050. Although prosthetics can significantly improve the quality of life for amputees by offering greater independence and preventing overuse injuries to the remaining limb, the reality is that many individuals either reduce their use or completely abandon their prosthetic devices.
Key Reasons for Prosthetic Abandonment
Several factors contribute to the high abandonment rates of upper limb prosthetics:
- Discomfort and Fit Issues: One of the primary reasons for prosthetic abandonment is discomfort. Users frequently report skin irritation, upper body pain, and other discomforts due to poor fit. Achieving an optimal fit is challenging and often limited by the number of iterations allowed by health insurance.
- Complexity and Usability: Prosthetics need to be user-friendly. Many devices fail to offer a natural and fluent experience, which can deter users from consistent use. Complex control mechanisms and the need for extensive mental effort to operate the device add to the problem.
- Lack of Sensory Feedback: Sensory feedback is crucial for performing daily tasks. Without tactile feedback, users must rely on visual and auditory cues, which increases cognitive load and makes simple tasks more challenging.
- Predictability and Control: Unpredictable behavior of the prosthetic device, such as unintended movements due to crosstalk of EMG signals, can lead to frustration and abandonment.
The Role of Technology and Training
While technological advancements have led to improved prosthetics, the focus must shift towards addressing user-centric challenges:
- Enhanced Sensory Feedback: Implementing advanced feedback mechanisms, such as vibrotactile stimulation, can help users better control and perceive the actions of their prosthetic devices.
- User-Centered Design: Prosthetic design should prioritize the needs and preferences of users. This involves creating devices that are comfortable, intuitive to use, and provide a natural range of motion.
- Comprehensive Training: Effective use of prosthetics requires thorough training. Early and ongoing training can help users become proficient in using their devices, reducing the likelihood of abandonment.
- Adaptive Devices: Devices that can offer greater flexibility and functionality, catering to a broader range of user needs.
Moving Forward
Understanding the reasons behind prosthetic abandonment is the first step towards improving prosthetic design and user experience. By focusing on comfort, usability, and user feedback, we can develop prosthetic devices that not only meet the functional needs of users but also enhance their overall quality of life.
At Marins Med, we are committed to advancing prosthetic technology and providing comprehensive support to ensure that every individual with limb loss can lead a fulfilling and independent life. Through continuous research and collaboration with users, we aim to overcome the challenges of prosthetic abandonment and pave the way for more effective and user-centric prosthetic solutions.
